Hashima: The Ghost Island
All mine
Brian Burke-Gaffney
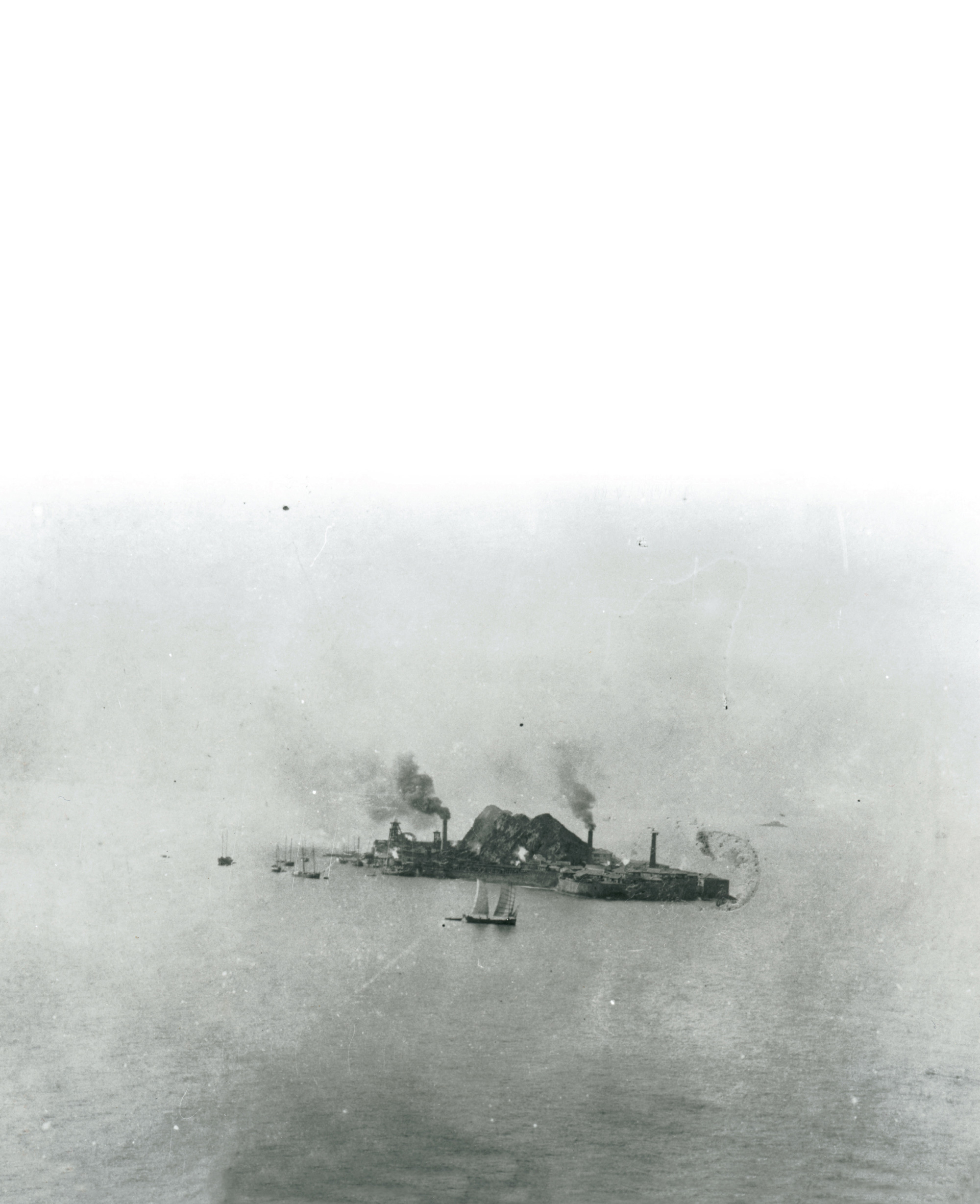

Seen from a distance, Hashima Island might be mistaken for the Japanese counterpart of Alcatraz rising from the ocean like a ragged slab of concrete, or perhaps a gambling resort with deserted hotels. Few casual observers would ever guess that, only 40 years ago, this tiny island was the site of a thriving community with the highest population density on earth.
One among 505 uninhabited islands in Nagasaki Prefecture, Hashima lies in the East China Sea some 15 kilometers from Nagasaki, its naked crags striking a stark contrast with the verdant peaks of nearby islands. A closer look reveals clusters of unpopulated high-rise buildings pressing up against a man-made sea wall, a battered shrine at the top of a steep rock cliff, and not a single tree in sight.
The clue to the island’s mystery lies in coal mining. Reached by long descending tunnels, coal beds below the bottom of the ocean near Hashima disgorged huge quantities of high-grade coal for almost a century. But in 1974 the inhabitants abandoned the island to the wind and salt spray, leaving behind only unneeded belongings and a few stray cats that could not be captured.
When transportation networks improved in the 18th and 19th centuries, the people of Takashima began to sell their coal abroad, primarily to salt-makers on the coast of the Seto Inland Sea. One of Japan’s most important industries at the time, salt-making, had relied traditionally on resin-rich pinewood as a fuel to boil seawater, but it was suffering from the ongoing depletion of pine forests. Coal was deemed the ideal alternative to pinewood.
At the time, Takashima Island was part of a feudal domain administered by the Fukahori Family, a branch of the Nabeshima Clan of present-day Saga Prefecture. Seeing the profits gleaned from the coal trade, the Fukahori Family usurped the management rights, assigned the islanders the role of subcontractor and labor force, and established coal profits as one of the pillars of the local economy.
This system was still firmly in place when Japan opened its doors to the world in the late 1850s and Nagasaki gained new importance as the closest port to China and a stopover for foreign commercial ships and naval vessels. This was also a time when Britain, America, and other Western countries were replacing their sail-rigged tea clippers and warships with steam-driven ships. The resulting demand for coal prompted Nabeshima Naomasa, lord of the Nabeshima Clan, to expand production capacity of the mine on Takashima.
Nabeshima turned to Scottish merchant Thomas B. Glover (1838-1911) for help. Until then, the coal- mining method on Takashima had been primitive: miners simply chipped away at exposed surfaces with picks and then moved on to other sites when the coal ran out or the holes became too deep to dig safely. But Glover imported modern mining equipment from Britain and hired British mining engineers to drill a vertical-shaft mine on the island. In April 1869, the drillers struck a coal bed some 45 meters underground, and Japan’s first modern coal mine started production.
The enormous success of the Takashima coal mine filled Nagasaki coffers with foreign currency and sparked a rush to develop mines on nearby islands—including the until-then useless heap of rock called Hashima.
The years that followed witnessed a remarkable surge in Japan’s industrial capacity and military might, encouraged by victory in both the Sino-Japanese War (1894-1895) and Russo-Japanese War (1904-1905). At Hashima, Mitsubishi launched a project to tap the coal resources under the sea bottom, successfully sinking a 199-meter-long vertical shaft in 1895 and still another shaft in 1898. The company also utilized the slag from the mine to carry out a series of land reclamations, thereby creating flat space for industrial facilities and dormitories. Completed around 1907, the high sea-walls gave the island the appearance of a battleship riding the waves. The resemblance was so uncanny that a local newspaper reporter dubbed it Gunkanjima (Battleship Island), a nickname that soon replaced the official name in common parlance.
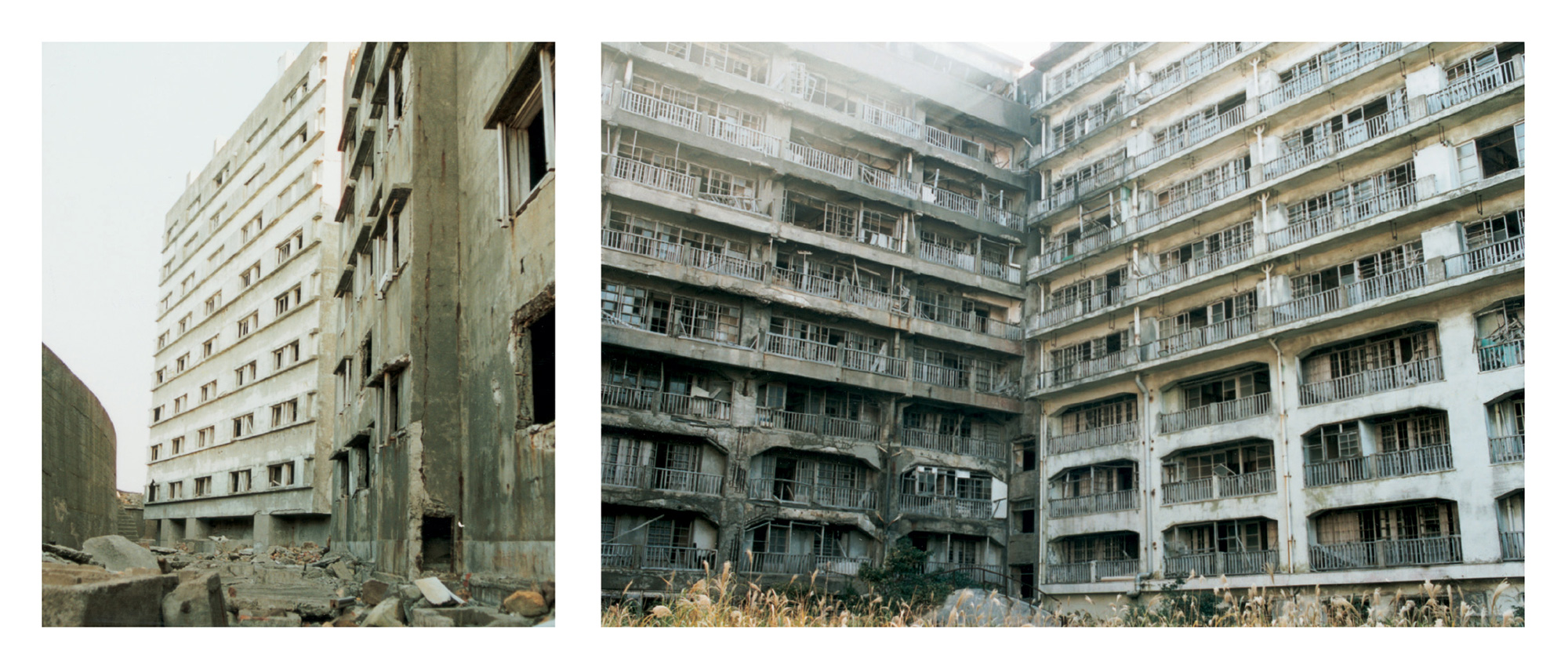
Hashima was producing about 150,000 tons of coal annually and its population had soared to over 3,000 when, in 1916, Mitsubishi built a reinforced concrete apartment block on the island to alleviate the lack of housing space and to prevent typhoon damage. This was Japan’s first concrete building of any significant size. America’s first large-scale concrete structure—the Ingalls Office Building, in Cincinnati—had been built only 14 years earlier.
A square, six-story structure built around a dingy inner courtyard at the southern edge of the island, the building provided cramped but private lodgings for the miners and their families. Each apartment consisted simply of a single, six-tatami-mat room (9.9 square meters) with a window, door, and small vestibule—more like a monk’s cell than an apartment, but still a major improvement over previous living quarters. Bathing, cooking, and toilet facilities were communal.
This building was followed two years later by an even larger apartment complex on the sloping rock at the center of the island. Then the tallest building in Japan, the E-shaped apartment block had nine stories on the ocean side and three on the rock side.
One multi-story apartment block followed another until the tiny island bristled with more than 30 concrete buildings. Even during the 11-year period before and during World War II, when not a single concrete building went up anywhere else in Japan, the construction of apartment blocks continued on Hashima as part of national efforts to meet the tremendous wartime demand for coal.
As a result of these efforts, Hashima’s annual coal production reached a peak of 410,000 tons in 1941. But it was an achievement that exacted a heavy toll in human suffering. While Japanese youth disappeared onto the battlefields of China, Southeast Asia, and the Pacific, the Japanese government forcibly recruited large numbers of Koreans and Chinese to fill the empty places in its factories and mines, and many of these men perished as a result of the harsh conditions and a starvation diet.
Hashima was no exception. By the time the atomic bomb rattled the windows on Hashima apartment blocks and Japan surrendered to the Allied forces in August 1945, about 1,300 laborers had died on the island, some in underground accidents, others of illnesses related to exhaustion and malnutrition. Still others had chosen a quicker, less gruesome death by jumping over the sea-wall and trying in vain to swim to the mainland.
Suh Jung-woo, one of the Korean laborers fortunate enough to survive the ordeal, remembered Hashima in a 1983 interview:
I was one of two boys forced onto a truck in my village and taken to the government office, where several thousand other Koreans ranging in age from about fourteen to twenty had been gathered. After a night at an inn, we were taken by truck to a nearby city, then by train to the port at Pusan and ship from Pusan to Shimonoseki. About 300 members of the group, including myself, were then taken by train to Nagasaki, where we arrived the following morning. All of us were being sent to Hashima.
I had relatives in Japan, not only my parents in Nagoya but also family members living in Sasebo. I thought that no matter where I was sent in Japan I would be able to escape and find shelter with them. But as soon as I saw Hashima I lost all hope.
The island was surrounded by high concrete walls, and there was ocean, nothing but ocean, all around. It was crowded with concrete buildings as high as nine stories.... We Koreans were lodged in buildings on the edge of the island. Seven or eight of us were put together in a tiny room, giving each person no more than a few feet of space.
The buildings were made of reinforced concrete and had mortar on the outside, but the interior was filthy and falling apart.... We were given uniforms like rice bags to wear and forced to begin work the morning after arrival. We were constantly watched and ordered around by Japanese guards, some of whom were wearing swords.
The mine was deep under the sea, the workers reaching it by elevator down a long narrow shaft. The coal was carried out from a spacious underground chamber, but the digging places were so small that we had to crouch down to work. It was excruciating, exhausting labor. Gas collected in the tunnels, and the rock ceilings and walls threatened to collapse at any minute. I was convinced that I would never leave the island alive.
Four or five workers in fact died every month in accidents. Modern concepts of safety were nonexistent. The corpses were cremated on Nakanoshima, the little island beside Hashima.

The end of World War II brought radical changes to Hashima Island and an important new purpose for its product. Instead of fuel for warships and steel for cannon shells, the coal from Hashima forged the tools for Japan’s recovery from the pit of humiliation and defeat. Ironically, however, it was another conflict—the Korean War (1950-1953)—that catapulted the coal mines, and virtually every other Japanese industry, into a golden period of prosperity and growth.
The population of Hashima reached a peak of 5,259 in 1959. People were literally jammed into every nook and corner of the apartment blocks. The rocky slopes holding most of these buildings comprised about 60 percent of the total island area of 6.3 hectares (15.6 acres), while the flat property reclaimed from the sea was used mostly for industrial facilities and made up the remaining 40 percent. At 835 people per hectare for the whole island, or an incredible 1,391 per hectare for the residential district, it is said to be the highest population density ever recorded in the world. Even Warabi, a Tokyo bedtown and the most densely populated city in modern Japan, notches up only 141 people per hectare.
Hashima contained all the facilities and services necessary for the subsistence of this bulging community. Elbowing for space in the shadows of the apartment blocks were a primary school, junior high school, playground, gymnasium, pinball parlor, movie theater, bars, restaurants, 25 different retail shops, hospital, hairdresser, Buddhist temple, Shinto shrine, and even a brothel. Motor vehicles were nonexistent. As one former miner put it, one could walk between any two points on the island in less time than it took to finish a cigarette. Umbrellas were also unnecessary: a labyrinth of corridors and staircases connected all the apartment blocks and served as the island’s highway system.
Equality may have reigned in the corridors, but the allocation of apartments reflected a rigid hierarchy of social classes. Unmarried miners and employees of subcontracting companies were interned in the old one-room apartments; married Mitsubishi workers and their families had apartments with two, six-mat rooms but shared toilets, kitchens and baths; high-ranking office personnel and teachers enjoyed the luxury of two-bedroom apartments with kitchens and flush toilets. The manager of Mitsubishi Hashima Coal Mine, meanwhile, lived in the only private, wood-constructed residence on the island—a house located symbolically at the summit of Hashima’s original rock.
Indeed, Mitsubishi owned the island and everything on it, running a kind of benevolent dictatorship that guaranteed job security and doled out free housing, electricity and water but demanded that residents take turns in the cleaning and maintenance of public facilities. Thus the people of Hashima huddled together, all under the wing of “The Company” and all bent on a common purpose.
But coal is not edible. The community depended completely on the outside world for food, clothing and other staples. Even fresh water had to be carried to the island until pipes along the sea floor connected it to mainland reservoirs in 1957. Any storm that prevented the passage of ships for more than a day spelled fear and austerity for Hashima.
The most notable feature of the island was the complete absence of soil and indigenous vegetation. Hashima, after all, was nothing more than a rim of coal slag packed around the circumference of a bare rock. A movie shot there by Shochiku Co. Ltd. in 1949 was aptly entitled Midori Naki Shima (The Greenless Island).
The initiation of a planting campaign in 1963 was a sign of the residents’ first hard-won taste of leisure. Using soil from the mainland they made gardens on the rooftops and enjoyed the unprecedented pleasure of home-grown vegetables and flowers. It was around this same time that electric rice cookers, refrigerators and television sets became standard appliances in the island’s apartments.
But the optimism did not last long. Hashima’s fortunes started on a downhill slide in the late 1960s when Japan’s economy soared and petroleum replaced coal as the pillar of national energy policies. Coal mines across the country began to close. Mitsubishi slashed the work force at Hashima step by step, retraining workers and sending them off to other branches of its sprawling and booming industrial network. The coup de grâce came on 15 January 1974, when the company held a ceremony in the island gymnasium and officially announced the closing of the mine.
The subsequent exodus proceeded with amazing speed. The last resident stepped onto the ship for Nagasaki on 20 April 1974, holding an umbrella up to a light rain and glancing back woefully toward the empty apartment blocks.
During its 84-year career under Mitsubishi, the island produced some 16.5 million tons of coal. The miners tunneled deep into the sea bottom, the builders carefully utilized every precious square meter of island property, and the islanders made valiant efforts to lead a comfortable and dignified life. But few, if any, of these people included the closing of the mine in their plans.
In that sense, the dead island of Hashima delivers a lively warning about the importance of foresight. It offers a view of the end result of “development,” the fate of a community severed from Mother Earth and engaged in a way of life disconnected from its food supply. In short, Hashima is what the world will be like when we finish urbanizing and exploiting it: a ghost planet spinning through space—silent, naked, and useless.
See press about “Hashima: The Ghost Island” on artinfo.com.
Note: There is currently a documentary on Hashima Island under production for Swedish television. The directors are Carl Michael von Hausswolff and Thomas Nordanstad.
Brian Burke-Gaffney was born in Canada in 1950 and came to Japan in 1972. He has been professor at the Nagasaki Institute of Applied Science since 1996.
Spotted an error? Email us at corrections at cabinetmagazine dot org.
If you’ve enjoyed the free articles that we offer on our site, please consider subscribing to our nonprofit magazine. You get twelve online issues and unlimited access to all our archives.